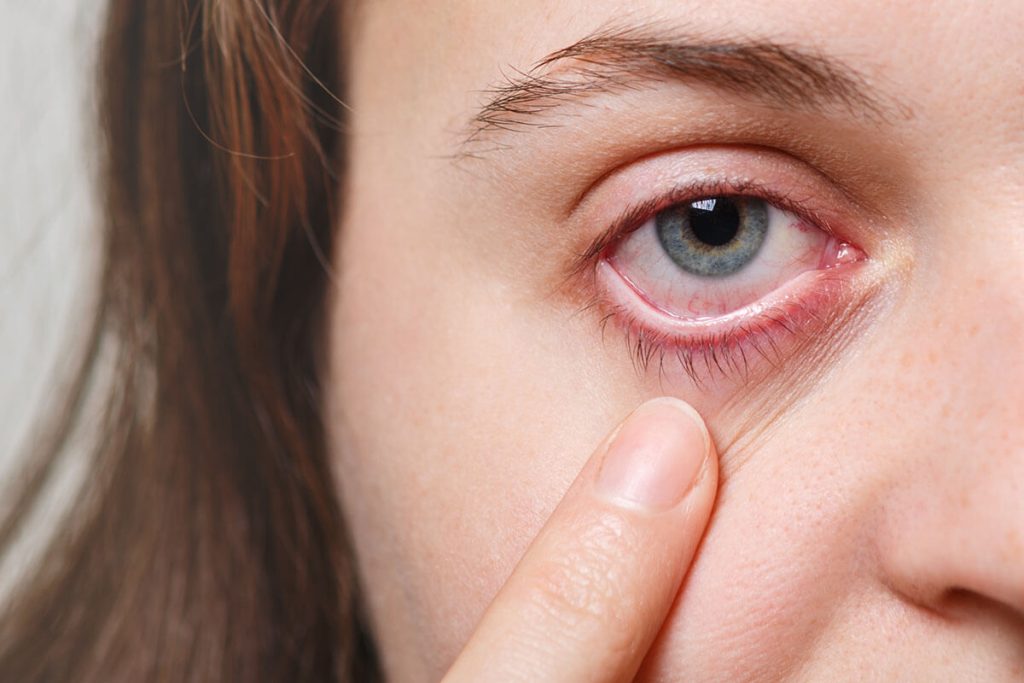
Uveitis, a severe eye condition characterized by inflammation, is also known as iridocyclitis. Accurate diagnosis and effective treatment are essential for managing this eye disease. This article will elucidate the nature of uveitis, its various types, as well as the symptoms and methods employed for treatment.
Unveiling Uveitis
Uveitis, characterized by inflammation within the eye, manifests in three distinct types—namely, anterior, intermediate, and posterior uveitis—each contingent on the specific region affected. Furthermore, the condition is categorized into acute uveitis for newly emerging cases and chronic uveitis for prolonged or frequently recurrent instances.
Anterior Uveitis:Characterized by inflammation within the iris tissue, specifically the pupil, anterior uveitis is identified by its focal point in this area.
Intermediate Uveitis: Inflammation that develops within the ciliary body, situated just behind the iris tissue, is termed intermediate uveitis.
Posterior Uveitis: When uveitis affects the choroid tissue located beyond the ciliary body, it is categorized as posterior uveitis.
Uveitis Attacks: Understanding the Onset
Uveitis, marked by periodic attacks, exhibits varied manifestations depending on the specific type afflicting an individual.
Exploring the Causes of Uveitis: A Dual Perspective
Uveitis is attributed to two main categories of causes: infectious and non-infectious. In cases of non-infectious uveitis, the specific origin remains elusive, often positioning the disorder as an autoimmune affliction exclusive to the eyes. This condition may be associated with autoimmune diseases like Behçet’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis, sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, or Crohn’s disease.
Conversely, infectious uveitis can arise subsequent to infections such as toxoplasmosis, cat scratch disease, herpes zoster virus, syphilis, or tuberculosis. Additionally, uveitis may uncommonly emerge as a side effect of medication, post-eye injury or surgery, and in conjunction with ocular cancers such as lymphoma. Understanding the diverse origins of uveitis is pivotal for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies.
Recognizing Uveitis: Symptoms during an Attack
During a uveitis episode, individuals may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Eye Pain: Sensations of discomfort or pain in the affected eye.
- Redness: Noticeable redness in one or both eyes.
- Light Sensitivity: Heightened sensitivity to light, known as photophobia.
- Floaters: Dark spots or specks drifting in the field of vision.
- Decreased Vision or Loss of Vision: Vision may become blurred, hazy, or, in severe cases, lead to a partial or complete loss of vision.
Being vigilant about these symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention and effective management of uveitis.
Diagnosing Uveitis: Insight into Diagnostic Methods
Uveitis diagnosis involves a comprehensive eye examination, where meticulous scrutiny of ocular structures is conducted. In addition to this, various imaging tests, including blood tests, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be prescribed to discern underlying factors contributing to the condition. These diagnostic measures collectively contribute to a thorough understanding of uveitis, facilitating targeted and effective treatment strategies.
Uveitis Treatment: Tailoring Solutions to Diverse Causes
Given the diverse causes of uveitis, the approach to treatment is multifaceted. Identification of the specific factor triggering uveitis guides the selection of an appropriate treatment strategy. Once the underlying cause is pinpointed, targeted interventions are applied to address and alleviate the root cause, ensuring a more effective and personalized therapeutic outcome.
Frequently Asked Questions About Uveitis
Explore common queries about uveitis below:
Is There a Herbal Treatment for Uveitis?
No, there is currently no herbal treatment specifically recognized for uveitis.
What are Beneficial Foods for Uveitis?
Recent studies suggest potential benefits for individuals with autoimmune uveitis by incorporating kefir, homemade yogurt, or direct probiotics rich in probiotic content into their diet. While not a definitive prescription, this nutritional approach has shown promise in certain autoimmune disorders. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary recommendations tailored to individual health conditions.